韩家淮
 韩家淮 HAN Jiahuai, Ph.D.
韩家淮 HAN Jiahuai, Ph.D.
教授,博士生导师
电 话:0592-2189390 0592-2189390
0592-2189390
E-mail: jhan@xmu.edu.cn
实验室网址:http://210.34.20.62/
1978-1982年,北京大学学士学位;
1982-1985年,北京大学硕士学位;
1990年,比利时布鲁塞尔大学,博士学位;
1990至1992年,美国德克萨斯大学西南医学中心博士后;
1993至2007年,历任美国Scripps研究所助理教授、副教授、教授;
2001年11至2007年7月,兼任厦门大学特聘教授;
2007年8月至今,厦门大学生命科学学院教授;
厦门大学医学与生命科学学部主任;
细胞应激生物学国家重点实验室主任。
1978-1982, Beijing University (Peking University), China, B.S., Specialty in Biochemistry
1982-1985, Beijing University (Peking University), China, M. S., Specialty in Protein Chemistry
1985-1990, University of Brussels (Université Libre de Bruxelles), Belgium, 1990, Ph.D., Specialty in Molecular Biology
1990-1992, Research Fellow, Department of Internal Medicine and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, Dallas, Texas, USA
1992-1993, Research Associate, Department of Immunology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, California, USA
1993-1996, Assistant Member, Department of Immunology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, California, USA
1996-2004, Associate Professor, Department of Immunology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, California, USA
2004-2007, Professor, Department of Immunology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, California, USA
2002- 2007, Adj. Professor, School of Life Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
2007 to present, Professor, School of Life Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
Dean, Faculty of Medicine and Life Sciences, Xiamen University, China
Director, State Key Laboratory of Cellular Stress Biology
研究领域(Research Area)
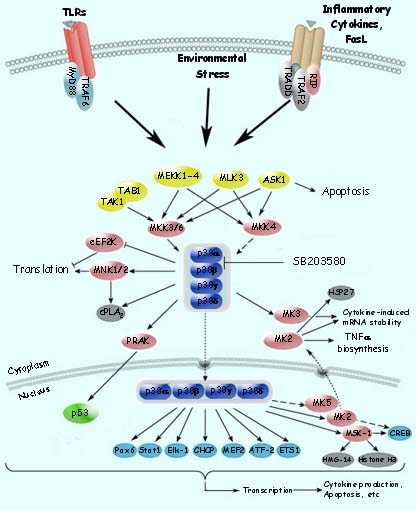 本实验室主要关注细胞应激反应在生理病理过程中的作用。主要用大规模基因突变和基因敲除的方法寻找关键的基因,并在细胞水平和两种模式生物——小鼠和果蝇上进行验证。然后分析这些基因及它们所介导的信号通道在应激反应中的作用。
本实验室主要关注细胞应激反应在生理病理过程中的作用。主要用大规模基因突变和基因敲除的方法寻找关键的基因,并在细胞水平和两种模式生物——小鼠和果蝇上进行验证。然后分析这些基因及它们所介导的信号通道在应激反应中的作用。
细胞应激反应(Cellular Stress responses)是细胞对不同的环境压力所产生的共同反应。外界感染以及内部病变所引起的应激反应是免疫炎症的重要组成部分,在许多人类重大疾病如肿瘤的发生发展中起着非常重要的作用。
细胞应激反应涉及很多生理过程,我们拟解决以下问题:
1. 细胞应激反应在细胞分化、细胞衰老、细胞凋亡和坏死的关系
2. 细胞应激反应和细胞癌变相关信号通路的关系
3. 细胞应激反应和肿瘤细胞代谢通路的关系
4. 免疫炎症和动脉粥样硬化、脓血症、肠炎与肠癌这些疾病的关系
Our research interests are the molecular mechanisms in cellular stress responses including inflammation and inflammation related diseases. Specifically, we are interested in:
1.The relationship between cellular stress responses and cell differentiation, senescence and death.
2.The relationship between cellular stress responses and malignancy.
3.The relationship between cellular stress responses and metabolic pathways.
4.The functions of cellular stress response pathways in septic shock, atherosclerosis, colitis and other inflammation related disease.
代表性论文(Selected Publications):
1. Lin J, Li H, Yang M, Ren J, Huang Z, Han F, Huang J, Ma J, Zhang D, Zhang Z, Wu J, Huang D, Qiao M, Jin G, Wu Q, Huang Y, Du J, Han J. A Role of RIP3-Mediated Macrophage Necrosis in Atherosclerosis Development.Cell Rep. 2013; 3(1): 200-10.
2. Zheng M, Wang YH, Wu XN, Wu SQ, Lu BJ, Dong MQ, Zhang HB, Naoto Yoshizuka, Sun PQ, Lin SC, Guan KL, and Han J. Inactivation of Rheb by PRAK-mediated phosphorylation is essential for energy depletion induced suppression of mTOR. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(3): 263-72.
3. Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ, Lin SC, Dong MQ, Han J. RIP3, an Energy Metabolism Regulator That Switches TNF-Induced Cell Death from Apoptosis to Necrosis. Science. 2009; 325, 332-336.
4. Otsuka M, Jing Q, Georgel P, New L, Chen J, Mols J, Kang YJ, Jiang Z, Du X, Das SC, Pattnaik AK, Beutler B, and Han J. Hypersusceptibility to vesicular stomatitis virus infection in Dicer-deficient mice is due to impaired miR24 and miR93 expression. Immunity. 2007; 27(1): 123-34.
5. Kang YJ, Kim SO, Shimada S, Otsuka M, Kwon BS, Watts TH, Han J. Cell Surface 4-1BBL mediates a sequential signaling pathway ‘downstream’ of TLR and is required for sustained TNF production in macrophages. Nature Immunol. 2007; 8 (6): 601-609.
6. Sun P, Yoshizuka N, New L, Moser BA, Li Y, Liao R, Xie C, Chen J, Deng Q, Yamout M, Dong M-Q, Frangou CG, Yates III JR, Wright PE, Han J. PRAK is essential for ras-induced senescence and tumor suppression.Cell. 2007; 128(2): 295-308.
7. Jing Q., Huang S., Guth S., Zarubin T., Motoyama A., Chen J., Di Padova F., Lin S-C., Gram H., and Han J. Involvement of microRNA in AU-rich element-mediated mRNA instability. Cell 2005; 120, 623-634.
8. Ge B., Gram H., Di Padova F., Huang B., New L., Ulevitch R. J., Luo Y. and Han J. MAP kinase kinase-independent activation of p38α mediated by TAB1-dependent autophosphorylation of p38α. Science2002; 295: 1291-4.
9. Huang S., Jiang Y., Li Z., Lin S., Ulevitch R. J., Nemerow G. and Han J. Apoptosis signaling pathway in T cells is composed of ICE/Ced-3 family proteases and MAP kinase kinase 6b. Immunity 1997; 6: 739-749.
10. Han J., Jiang Y., Li Z., Kravchenko V.V. and Ulevitch R. J. Activation of the transcription factor MEF2C by the MAP kinase p38 in inflammation. Nature 1997; 386: 296-299.
11. Han J., Lee J.-D., Bibbs L. and Ulevitch R.J. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science 1994; 265:808-811.
荣誉、奖励及参加学术团体的情况(Honors and Awards, Profession service)
全国优秀博士论文(2012);
教育部自然科学研究一等奖 (2011);
“长江学者成就奖” (2009);
“药明康德生命化学研究奖”一等奖 (2009);
“卢嘉锡优秀导师奖” (2009);
美国心脏协会成熟研究员奖 (1995);
比利时Jean Stas奖 (1991);
基金委杰青(B类);
教育部长江学者;
中组部千人计划入选者。
专业期刊编委
Journal of Biological Chemistry前编委;
International Immunopharmacology前编委;
Protein & Cell 编委;
中国癌症研究编委。
专业学会会员
美国科学促进会会员(American Association for the Advancement of Science—AAAS);
美国分子生物学及生物化学学会会员(American Society for Molecular Biology and Biochemistry);
美国免疫学协会会员(The American Association of Immunologists);
美国微生物学协会会员(American Society for Microbiology);
国际内毒素协会会员(International Society of Endotoxin);
中国遗传学会国际交流委员会委员;
中国生物化学与分子生物学学会蛋白质专业委员会副主任委员;
中国免疫学会会员。附件列表
词条内容仅供参考,如果您需要解决具体问题
(尤其在法律、医学等领域),建议您咨询相关领域专业人士。
